Data
library(RCurl)
myCsv <- getURL("https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/8272421/stat/stat_one.txt",
ssl.verifypeer = FALSE)
mydata <- read.csv(textConnection(myCsv), sep = "\t")
mydata$subject <- factor(mydata$subject)
Create two subsets, control and concussed
concussed <- subset(mydata, condition == "concussed")
control <- subset(mydata, condition == "control")
Summary statistics
library(psych)
describe(mydata)
var n mean sd median trimmed mad min
subject* 1 40 20.50 11.69 20.50 20.50 14.83 1.00
condition* 2 40 1.50 0.51 1.50 1.50 0.74 1.00
verbal_memory_baseline 3 40 89.75 6.44 91.00 90.44 6.67 75.00
visual_memory_baseline 4 40 74.88 8.60 75.00 74.97 9.64 59.00
visual.motor_speed_baseline 5 40 34.03 3.90 33.50 34.02 3.62 26.29
reaction_time_baseline 6 40 0.67 0.15 0.65 0.66 0.13 0.42
impulse_control_baseline 7 40 8.28 2.05 8.50 8.38 2.22 2.00
total_symptom_baseline 8 40 0.05 0.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
verbal_memory_retest 9 40 82.00 11.02 85.00 82.97 9.64 59.00
visual_memory_retest 10 40 71.90 8.42 72.00 72.19 10.38 54.00
visual.motor_speed_retest 11 40 35.83 8.66 35.15 34.98 6.89 20.15
reaction_time_retest 12 40 0.67 0.22 0.65 0.65 0.13 0.19
impulse_control_retest 13 40 6.75 2.98 7.00 6.81 2.97 1.00
total_symptom_retest 14 40 13.88 15.32 7.00 12.38 10.38 0.00
max range skew kurtosis se
subject* 40.00 39.00 0.00 -1.29 1.85
condition* 2.00 1.00 0.00 -2.05 0.08
verbal_memory_baseline 98.00 23.00 -0.70 -0.51 1.02
visual_memory_baseline 91.00 32.00 -0.11 -0.96 1.36
visual.motor_speed_baseline 41.87 15.58 0.08 -0.75 0.62
reaction_time_baseline 1.20 0.78 1.14 2.21 0.02
impulse_control_baseline 12.00 10.00 -0.57 0.36 0.32
total_symptom_baseline 1.00 1.00 3.98 14.16 0.03
verbal_memory_retest 97.00 38.00 -0.65 -0.81 1.74
visual_memory_retest 86.00 32.00 -0.28 -0.87 1.33
visual.motor_speed_retest 60.77 40.62 0.86 0.65 1.37
reaction_time_retest 1.30 1.11 0.93 1.29 0.03
impulse_control_retest 12.00 11.00 -0.16 -1.06 0.47
total_symptom_retest 43.00 43.00 0.44 -1.47 2.42
describeBy(mydata, mydata$condition)
group: concussed
var n mean sd median trimmed mad min
subject* 1 20 30.50 5.92 30.50 30.50 7.41 21.00
condition* 2 20 1.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 1.00
verbal_memory_baseline 3 20 89.65 7.17 92.50 90.56 5.93 75.00
visual_memory_baseline 4 20 74.75 8.03 74.00 74.25 8.15 63.00
visual.motor_speed_baseline 5 20 33.20 3.62 33.09 33.27 3.32 26.29
reaction_time_baseline 6 20 0.66 0.17 0.63 0.64 0.13 0.42
impulse_control_baseline 7 20 8.55 1.64 9.00 8.62 1.48 5.00
total_symptom_baseline 8 20 0.05 0.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
verbal_memory_retest 9 20 74.05 9.86 74.00 73.88 11.86 59.00
visual_memory_retest 10 20 69.20 8.38 69.50 69.62 10.38 54.00
visual.motor_speed_retest 11 20 38.27 10.01 35.15 37.32 7.73 25.70
reaction_time_retest 12 20 0.78 0.23 0.70 0.74 0.11 0.51
impulse_control_retest 13 20 5.00 2.53 5.00 4.88 2.97 1.00
total_symptom_retest 14 20 27.65 9.07 27.00 27.75 11.12 13.00
max range skew kurtosis se
subject* 40.00 19.00 0.00 -1.38 1.32
condition* 1.00 0.00 NaN NaN 0.00
verbal_memory_baseline 97.00 22.00 -0.79 -0.70 1.60
visual_memory_baseline 91.00 28.00 0.45 -0.72 1.80
visual.motor_speed_baseline 39.18 12.89 -0.13 -0.78 0.81
reaction_time_baseline 1.20 0.78 1.38 2.41 0.04
impulse_control_baseline 11.00 6.00 -0.39 -0.81 0.37
total_symptom_baseline 1.00 1.00 3.82 13.29 0.05
verbal_memory_retest 91.00 32.00 0.07 -1.24 2.21
visual_memory_retest 80.00 26.00 -0.27 -1.26 1.87
visual.motor_speed_retest 60.77 35.07 0.77 -0.57 2.24
reaction_time_retest 1.30 0.79 1.09 -0.10 0.05
impulse_control_retest 11.00 10.00 0.39 -0.28 0.57
total_symptom_retest 43.00 30.00 -0.11 -1.25 2.03
--------------------------------------------------------
group: control
var n mean sd median trimmed mad min
subject* 1 20 10.50 5.92 10.50 10.50 7.41 1.00
condition* 2 20 2.00 0.00 2.00 2.00 0.00 2.00
verbal_memory_baseline 3 20 89.85 5.82 90.00 90.31 7.41 78.00
visual_memory_baseline 4 20 75.00 9.34 77.00 75.50 9.64 59.00
visual.motor_speed_baseline 5 20 34.86 4.09 34.39 34.85 4.92 27.36
reaction_time_baseline 6 20 0.67 0.13 0.66 0.67 0.13 0.42
impulse_control_baseline 7 20 8.00 2.41 7.50 8.12 2.22 2.00
total_symptom_baseline 8 20 0.05 0.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
verbal_memory_retest 9 20 89.95 4.36 90.50 90.06 5.19 81.00
visual_memory_retest 10 20 74.60 7.76 74.50 75.00 8.15 60.00
visual.motor_speed_retest 11 20 33.40 6.44 34.54 33.52 6.30 20.15
reaction_time_retest 12 20 0.57 0.16 0.56 0.57 0.13 0.19
impulse_control_retest 13 20 8.50 2.31 9.00 8.69 1.48 3.00
total_symptom_retest 14 20 0.10 0.31 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
max range skew kurtosis se
subject* 20.00 19.00 0.00 -1.38 1.32
condition* 2.00 0.00 NaN NaN 0.00
verbal_memory_baseline 98.00 20.00 -0.41 -0.87 1.30
visual_memory_baseline 88.00 29.00 -0.46 -1.27 2.09
visual.motor_speed_baseline 41.87 14.51 0.09 -1.19 0.91
reaction_time_baseline 1.00 0.58 0.47 -0.02 0.03
impulse_control_baseline 12.00 10.00 -0.41 -0.17 0.54
total_symptom_baseline 1.00 1.00 3.82 13.29 0.05
verbal_memory_retest 97.00 16.00 -0.25 -1.02 0.97
visual_memory_retest 86.00 26.00 -0.23 -1.11 1.73
visual.motor_speed_retest 44.28 24.13 -0.25 -0.77 1.44
reaction_time_retest 0.90 0.71 -0.16 0.06 0.04
impulse_control_retest 12.00 9.00 -0.73 -0.32 0.52
total_symptom_retest 1.00 1.00 2.47 4.32 0.07
Density plots
par(mfrow = c(1, 3))
hist(mydata$total_symptom_retest, xlab = "Total symptom score", main = "")
plot(density(mydata$total_symptom_retest), xlab = "Total sympton score", main = "")
# prob=TRUE for probabilities not counts
hist(mydata$total_symptom_retest, xlab = "Total symptom score", main = "", prob = TRUE)
lines(density(mydata$total_symptom_retest))
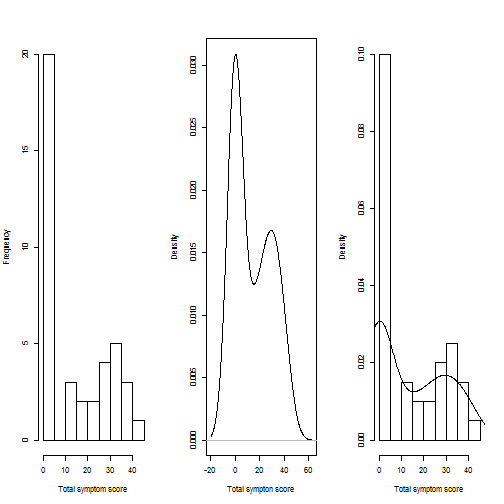
Compare density plots
library(sm)
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
# This function allows a set of univariate density estimates to be compared,
# both graphically and formally in a permutation test of equality.
sm.density.compare(mydata$total_symptom_retest, mydata$condition, xlab = "Total symptom score")
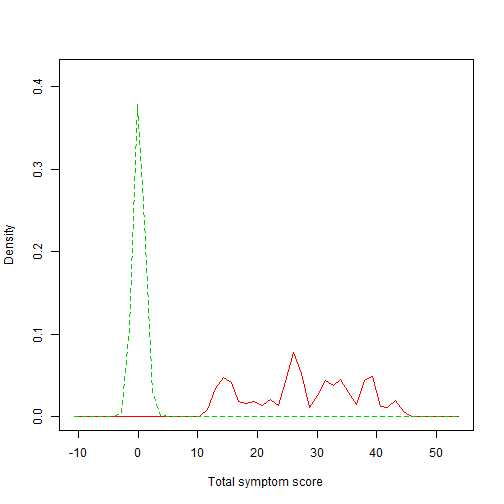
Correlation analysis of baseline measures
cor(mydata[3:8]) # Columns 3 to 8 contain the 6 baseline measures
verbal_memory_baseline visual_memory_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 1.00000 0.37512
visual_memory_baseline 0.37512 1.00000
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.04057 -0.23339
reaction_time_baseline 0.14673 0.13615
impulse_control_baseline 0.13147 0.23756
total_symptom_baseline 0.13521 0.01689
visual.motor_speed_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline -0.040567
visual_memory_baseline -0.233391
visual.motor_speed_baseline 1.000000
reaction_time_baseline -0.131955
impulse_control_baseline 0.005221
total_symptom_baseline -0.051903
reaction_time_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.1467
visual_memory_baseline 0.1361
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.1320
reaction_time_baseline 1.0000
impulse_control_baseline 0.1213
total_symptom_baseline -0.0339
impulse_control_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.131471
visual_memory_baseline 0.237559
visual.motor_speed_baseline 0.005221
reaction_time_baseline 0.121334
impulse_control_baseline 1.000000
total_symptom_baseline 0.082149
total_symptom_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.13521
visual_memory_baseline 0.01689
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.05190
reaction_time_baseline -0.03390
impulse_control_baseline 0.08215
total_symptom_baseline 1.00000
round(cor(mydata[3:8]), 2) # Round to 2 decimal places
verbal_memory_baseline visual_memory_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 1.00 0.38
visual_memory_baseline 0.38 1.00
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.04 -0.23
reaction_time_baseline 0.15 0.14
impulse_control_baseline 0.13 0.24
total_symptom_baseline 0.14 0.02
visual.motor_speed_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline -0.04
visual_memory_baseline -0.23
visual.motor_speed_baseline 1.00
reaction_time_baseline -0.13
impulse_control_baseline 0.01
total_symptom_baseline -0.05
reaction_time_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.15
visual_memory_baseline 0.14
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.13
reaction_time_baseline 1.00
impulse_control_baseline 0.12
total_symptom_baseline -0.03
impulse_control_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.13
visual_memory_baseline 0.24
visual.motor_speed_baseline 0.01
reaction_time_baseline 0.12
impulse_control_baseline 1.00
total_symptom_baseline 0.08
total_symptom_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 0.14
visual_memory_baseline 0.02
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.05
reaction_time_baseline -0.03
impulse_control_baseline 0.08
total_symptom_baseline 1.00
Color scatterplot matrix, colored and ordered by magnitude of r
library(gclus)
base <- mydata[3:8]
base.r <- abs(cor(base))
base.color <- dmat.color(base.r)
base.order <- order.single(base.r)
# This function draws a scatterplot matrix of data. Variables may be
# reordered and panels colored in the display
cpairs(base, base.order, panel.colors = base.color, gap = 0.5, main = "Variables Ordered and Colored by Correlation")
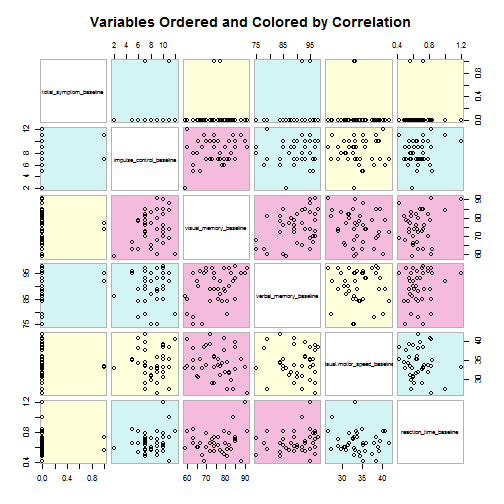
Regression analyses, unstandardized
model1 <- lm(mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline)
summary(model1)
Call:
lm(formula = mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-8.137 -2.553 -0.358 2.803 12.152
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 10.3386 6.5090 1.59 0.12
mydata$visual_memory_baseline 0.8222 0.0864 9.52 1.3e-11 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 4.64 on 38 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.705, Adjusted R-squared: 0.697
F-statistic: 90.6 on 1 and 38 DF, p-value: 1.32e-11
# Print 95% confidence interval for the regression coefficient
confint(model1)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -2.8381 23.5154
mydata$visual_memory_baseline 0.6473 0.9971
# Scatterplot with confidence interval around the regression line
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(mydata, aes(x = visual_memory_baseline, y = visual_memory_retest)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm") + geom_point()
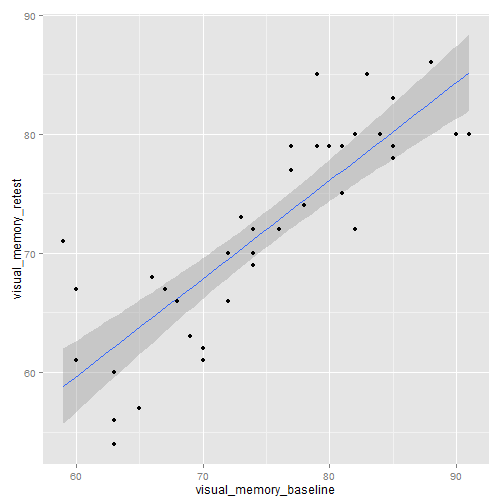
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
plot(mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline, main = "Scatterplot",
ylab = "retest", xlab = "baseline")
abline(model1, col = "blue")
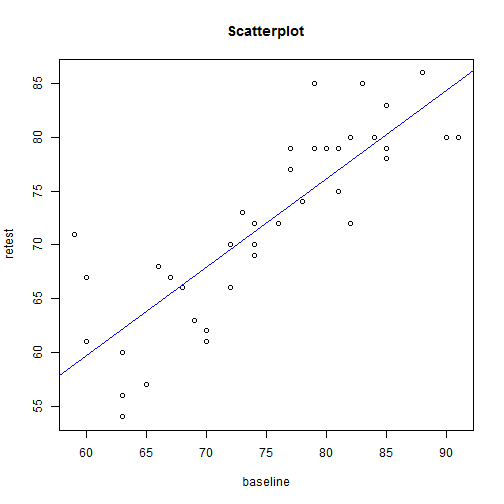
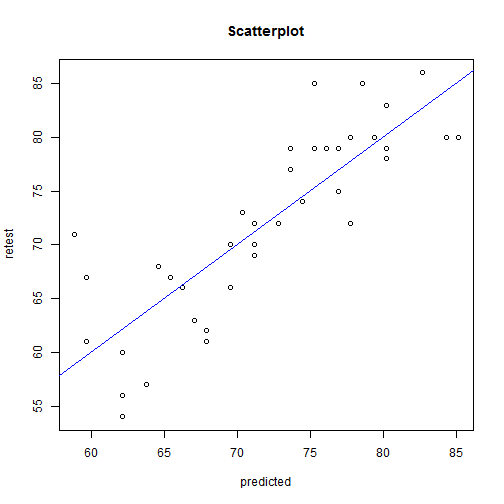
# To visualize model1, save the predicted scores as a new variable and then
# plot with endurance
mydata$predicted <- fitted(model1)
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
plot(mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$predicted, main = "Scatterplot", ylab = "retest",
xlab = "predicted")
abline(lm(mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$predicted), col = "blue")
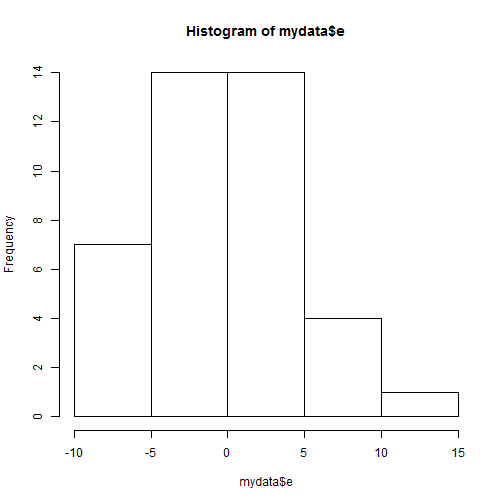
# The function fitted returns predicted scores whereas the function resid
# returns residuals
mydata$e <- resid(model1)
hist(mydata$e)
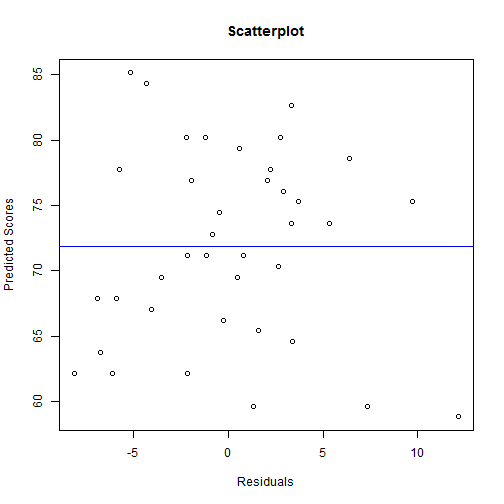
plot(mydata$predicted ~ mydata$e, main = "Scatterplot", ylab = "Predicted Scores",
xlab = "Residuals")
abline(lm(mydata$predicted ~ mydata$e), col = "blue")
# Conduct a model comparison NHST to compare the fit of model1 to the fit of
# model2
model2 <- lm(mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline + mydata$verbal_memory_baseline)
anova(model1, model2)
Analysis of Variance Table
Model 1: mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline
Model 2: mydata$visual_memory_retest ~ mydata$visual_memory_baseline +
mydata$verbal_memory_baseline
Res.Df RSS Df Sum of Sq F Pr(>F)
1 38 818
2 37 790 1 27.8 1.3 0.26
Regression analyses, standardized
# In simple regression, the standardized regression coefficient will be the
# same as the correlation coefficient
round(cor(mydata[3:5]), 2) # Round to 2 decimal places
verbal_memory_baseline visual_memory_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline 1.00 0.38
visual_memory_baseline 0.38 1.00
visual.motor_speed_baseline -0.04 -0.23
visual.motor_speed_baseline
verbal_memory_baseline -0.04
visual_memory_baseline -0.23
visual.motor_speed_baseline 1.00
model1.z <- lm(scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline))
summary(model1.z)
Call:
lm(formula = scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline))
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.9891 -0.5813 0.0866 0.7885 1.3377
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -2.63e-17 1.48e-01 0.00 1.000
scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) 3.75e-01 1.50e-01 2.49 0.017
(Intercept)
scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) *
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.939 on 38 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.141, Adjusted R-squared: 0.118
F-statistic: 6.22 on 1 and 38 DF, p-value: 0.0171
model2.z <- lm(scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline))
summary(model2.z)
Call:
lm(formula = scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline))
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.302 -0.730 0.146 0.826 1.327
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) -1.85e-17 1.60e-01 0.00
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline) -4.06e-02 1.62e-01 -0.25
Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 1.0
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline) 0.8
Residual standard error: 1.01 on 38 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.00165, Adjusted R-squared: -0.0246
F-statistic: 0.0626 on 1 and 38 DF, p-value: 0.804
model3.z <- lm(scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) +
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline))
summary(model3.z)
Call:
lm(formula = scale(mydata$verbal_memory_baseline) ~ scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) +
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline))
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.9657 -0.5620 0.0848 0.7847 1.3356
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) -4.48e-18 1.50e-01 0.00
scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) 3.87e-01 1.57e-01 2.47
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline) 4.97e-02 1.57e-01 0.32
Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 1.000
scale(mydata$visual_memory_baseline) 0.018 *
scale(mydata$visual.motor_speed_baseline) 0.753
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.95 on 37 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.143, Adjusted R-squared: 0.0967
F-statistic: 3.09 on 2 and 37 DF, p-value: 0.0575
NHST for each correlation coefficient
# Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST) is a statistical method for
# testing whether the factor we are talking about has the effect on our
# observation.
cor.test(mydata$visual_memory_baseline, mydata$visual_memory_retest)
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: mydata$visual_memory_baseline and mydata$visual_memory_retest
t = 9.519, df = 38, p-value = 1.321e-11
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
0.7147 0.9123
sample estimates:
cor
0.8394
Moderation analysis
myCsv <- getURL("https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/8272421/stat/stat_one_mod.txt",
ssl.verifypeer = FALSE)
MOD <- read.table(textConnection(myCsv), header = TRUE)
head(MOD)
subject condition IQ WM WM.centered D1 D2
1 1 control 134 91 -8.08 0 0
2 2 control 121 145 45.92 0 0
3 3 control 86 118 18.92 0 0
4 4 control 74 105 5.92 0 0
5 5 control 80 96 -3.08 0 0
6 6 control 105 133 33.92 0 0
# First, is there an effect of stereotype threat?
model_mod0 <- lm(MOD$IQ ~ MOD$D1 + MOD$D2)
summary(model_mod0)
Call:
lm(formula = MOD$IQ ~ MOD$D1 + MOD$D2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-51.88 -11.13 -0.45 8.77 43.12
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 97.88 2.29 42.8 <2e-16 ***
MOD$D1 -45.72 3.23 -14.2 <2e-16 ***
MOD$D2 -49.86 3.23 -15.4 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 16.2 on 147 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.666, Adjusted R-squared: 0.661
F-statistic: 147 on 2 and 147 DF, p-value: <2e-16
confint(model_mod0)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 93.36 102.40
MOD$D1 -52.11 -39.33
MOD$D2 -56.25 -43.47
# We could also use the aov function (for analysis of variance) followed by
# the TukeyHSD function (Tukey's test of pairwise comparisons, which adjusts
# the p value to prevent infaltion of Type I error rate)
table(MOD$condition)
control threat1 threat2
50 50 50
model_mod0a <- aov(MOD$IQ ~ MOD$condition)
summary(model_mod0a)
Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
MOD$condition 2 76558 38279 147 <2e-16 ***
Residuals 147 38393 261
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
# Create a set of confidence intervals on the differences between the means
# of the levels of a factor with the specified family-wise probability of
# coverage. The intervals are based on the Studentized range statistic,
# Tukey's ‘Honest Significant Difference’ method.
TukeyHSD(model_mod0a)
Tukey multiple comparisons of means
95% family-wise confidence level
Fit: aov(formula = MOD$IQ ~ MOD$condition)
$`MOD$condition`
diff lwr upr p adj
threat1-control -45.72 -53.37 -38.067 0.0000
threat2-control -49.86 -57.51 -42.207 0.0000
threat2-threat1 -4.14 -11.79 3.513 0.4082
# Moderation analysis (uncentered): model_mod1 tests for 'first-order
# effects'; model_mod2 tests for moderation
model_mod1 <- lm(MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2)
summary(model_mod1)
Call:
lm(formula = MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-47.34 -7.29 0.74 7.61 42.42
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 59.7864 7.1436 8.37 4.3e-14 ***
MOD$WM 0.3728 0.0669 5.57 1.2e-07 ***
MOD$D1 -45.2055 2.9464 -15.34 < 2e-16 ***
MOD$D2 -46.9074 2.9922 -15.68 < 2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 14.7 on 146 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.725, Adjusted R-squared: 0.719
F-statistic: 128 on 3 and 146 DF, p-value: <2e-16
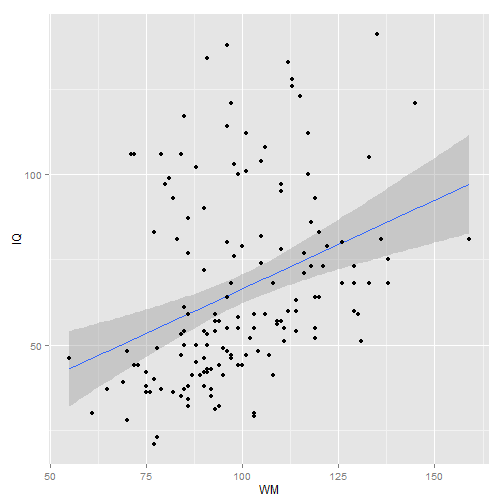
ggplot(MOD, aes(x = WM, y = IQ)) + geom_smooth(method = "lm") + geom_point()
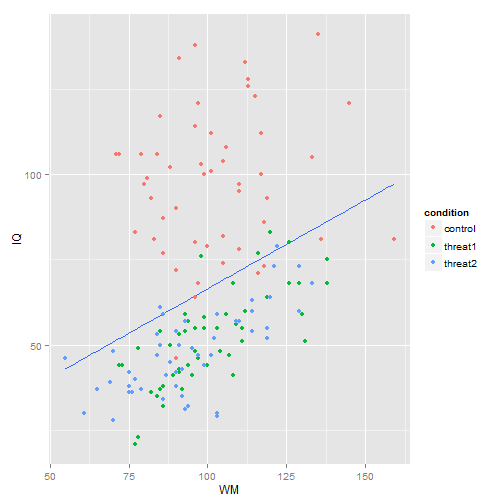
ggplot(MOD, aes(x = WM, y = IQ)) + stat_smooth(method = "lm", se = F) + geom_point(aes(color = condition))
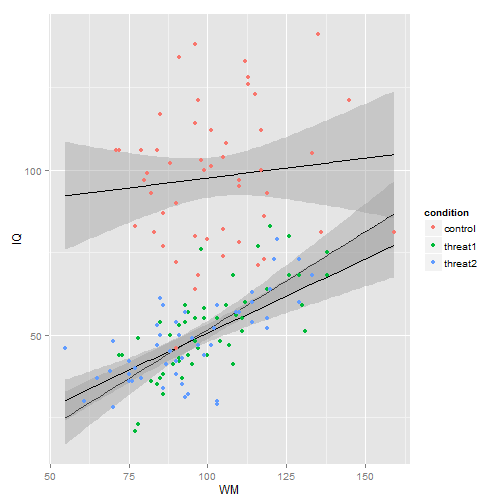
ggplot(MOD, aes(x = WM, y = IQ)) + geom_smooth(aes(group = condition), method = "lm",
se = T, color = "black", fullrange = T) + geom_point(aes(color = condition))
# Create new predictor variables
MOD$WM.D1 <- (MOD$WM * MOD$D1)
MOD$WM.D2 <- (MOD$WM * MOD$D2)
model_mod2 <- lm(MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2 + MOD$WM.D1 + MOD$WM.D2)
summary(model_mod2)
Call:
lm(formula = MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2 + MOD$WM.D1 +
MOD$WM.D2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-50.41 -7.18 0.42 8.20 40.86
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 85.585 11.358 7.54 5.0e-12 ***
MOD$WM 0.120 0.109 1.10 0.2730
MOD$D1 -93.095 16.857 -5.52 1.5e-07 ***
MOD$D2 -79.897 15.477 -5.16 8.0e-07 ***
MOD$WM.D1 0.472 0.164 2.88 0.0046 **
MOD$WM.D2 0.329 0.155 2.13 0.0353 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 14.4 on 144 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.741, Adjusted R-squared: 0.732
F-statistic: 82.4 on 5 and 144 DF, p-value: <2e-16
anova(model_mod1, model_mod2)
Analysis of Variance Table
Model 1: MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2
Model 2: MOD$IQ ~ MOD$WM + MOD$D1 + MOD$D2 + MOD$WM.D1 + MOD$WM.D2
Res.Df RSS Df Sum of Sq F Pr(>F)
1 146 31655
2 144 29784 2 1871 4.52 0.012 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Mediation analysis
myCsv <- getURL("https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/8272421/stat/stat_one_med.txt",
ssl.verifypeer = FALSE)
MED <- read.table(textConnection(myCsv), header = TRUE)
head(MED)
subject condition IQ WM
1 1 control 73 37
2 2 control 128 77
3 3 control 83 32
4 4 control 83 33
5 5 control 64 53
6 6 control 95 46
# The function sobel in the multilevel package executes the entire mediation
# analysis in one step but first we will do it with 3 lm models
model.YX <- lm(MED$IQ ~ MED$condition)
model.YXM <- lm(MED$IQ ~ MED$condition + MED$WM)
model.MX <- lm(MED$WM ~ MED$condition)
summary(model.YX)
Call:
lm(formula = MED$IQ ~ MED$condition)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-35.32 -9.57 -1.82 10.68 39.68
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 97.32 2.07 47.00 < 2e-16 ***
MED$conditionthreat -11.00 2.93 -3.76 0.00029 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 14.6 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.126, Adjusted R-squared: 0.117
F-statistic: 14.1 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 0.000293
summary(model.YXM)
Call:
lm(formula = MED$IQ ~ MED$condition + MED$WM)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-31.88 -7.90 0.93 6.99 27.58
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 55.998 4.644 12.06 < 2e-16 ***
MED$conditionthreat -2.408 2.316 -1.04 0.3
MED$WM 0.752 0.080 9.41 2.6e-15 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 10.6 on 97 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.543, Adjusted R-squared: 0.533
F-statistic: 57.6 on 2 and 97 DF, p-value: <2e-16
summary(model.MX)
Call:
lm(formula = MED$WM ~ MED$condition)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-31.92 -7.75 -0.50 10.18 30.50
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 54.92 1.90 28.89 < 2e-16 ***
MED$conditionthreat -11.42 2.69 -4.25 4.9e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 13.4 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.156, Adjusted R-squared: 0.147
F-statistic: 18 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 4.91e-05
# Compare the results to the output of the sobel function
library(multilevel)
# Estimate Sobel's (1982) indirect test for mediation. The function
# provides an estimate of the magnitude of the indirect effect, Sobel's
# first-order estimate of the standard error associated with the indirect
# effect, and the corresponding z-value.
model.ALL <- sobel(MED$condition, MED$WM, MED$IQ)
model.ALL
$`Mod1: Y~X`
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 97.32 2.071 46.999 4.966e-69
predthreat -11.00 2.928 -3.756 2.928e-04
$`Mod2: Y~X+M`
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 55.9977 4.644 12.058 5.304e-21
predthreat -2.4075 2.316 -1.039 3.012e-01
med 0.7524 0.080 9.406 2.577e-15
$`Mod3: M~X`
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 54.92 1.901 28.895 9.487e-50
predthreat -11.42 2.688 -4.249 4.906e-05
$Indirect.Effect
[1] -8.593
$SE
[1] 2.219
$z.value
[1] -3.872
$N
[1] 100
Conduct group comparisons with both parametric and non-parametric tests
myCsv <- getURL("https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/8272421/stat/stat_one_t_anova.txt",
ssl.verifypeer = FALSE)
wm <- read.table(textConnection(myCsv), header = TRUE)
head(wm)
cond pre post gain train
1 t08 8 9 1 1
2 t08 8 10 2 1
3 t08 8 8 0 1
4 t08 8 7 -1 1
5 t08 9 11 2 1
6 t08 9 10 1 1
# Create two subsets of data: One for the control group and another for the
# training groups
wm.c = subset(wm, wm$train == "0")
wm.t = subset(wm, wm$train == "1")
# Dependent t-tests and Wilcoxan
# First, compare pre and post scores in the control group
t.test(wm.c$pre, wm.c$post, paired = T)
Paired t-test
data: wm.c$pre and wm.c$post
t = -9.009, df = 39, p-value = 4.511e-11
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-2.418 -1.532
sample estimates:
mean of the differences
-1.975
# Wilcoxon Rank Sum and Signed Rank Tests Performs one- and two-sample
# Wilcoxon tests on vectors of data; the latter is also known as
# ‘Mann-Whitney’ test.
wilcox.test(wm.c$pre, wm.c$post, paired = T)
Wilcoxon signed rank test with continuity correction
data: wm.c$pre and wm.c$post
V = 10, p-value = 1.717e-07
alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
# Next, compare pre and post scores in the training groups
t.test(wm.t$pre, wm.t$post, paired = T)
Paired t-test
data: wm.t$pre and wm.t$post
t = -14.49, df = 79, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-3.966 -3.009
sample estimates:
mean of the differences
-3.487
# Wilcoxon
wilcox.test(wm.t$pre, wm.t$post, paired = T)
Wilcoxon signed rank test with continuity correction
data: wm.t$pre and wm.t$post
V = 10, p-value = 3.017e-14
alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
# Cohen's d for dependent t-tests
library(lsr)
cohensD(wm.c$post, wm.c$pre, method = "paired")
[1] 1.424
cohensD(wm.t$post, wm.t$pre, method = "paired")
[1] 1.62
# Independent t-test and Mann Whitney
# Compare the gain scores in the control and training groups
t.test(wm$gain ~ wm$train, var.equal = T)
Two Sample t-test
data: wm$gain by wm$train
t = -4.04, df = 118, p-value = 9.539e-05
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-2.2538 -0.7712
sample estimates:
mean in group 0 mean in group 1
1.975 3.487
# Mann-Whitney
wilcox.test(wm$gain ~ wm$train, paired = F)
Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
data: wm$gain by wm$train
W = 916, p-value = 0.0001061
alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
# Cohen's d for independent t-tests
cohensD(wm$gain ~ wm$train, method = "pooled")
[1] 0.7824
# Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Kruskul Wallis To compare the gain scores
# across all groups, use ANOVA First, check the homogeneity of variance
# assumption
library(car)
leveneTest(wm.t$gain, wm.t$cond, center = "mean")
Levene's Test for Homogeneity of Variance (center = "mean")
Df F value Pr(>F)
group 3 1.13 0.34
76
leveneTest(wm.t$gain, wm.t$cond)
Levene's Test for Homogeneity of Variance (center = median)
Df F value Pr(>F)
group 3 1.31 0.28
76
aov.model = aov(wm.t$gain ~ wm.t$cond)
summary(aov.model)
Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
wm.t$cond 3 213 71 35.3 2.2e-14 ***
Residuals 76 153 2
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
# Kruskal Wallis Rank Sum Test
kruskal.test(wm.t$gain ~ wm.t$cond)
Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
data: wm.t$gain by wm.t$cond
Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 50.25, df = 3, p-value = 7.084e-11
# Effect size for ANOVA
etaSquared(aov.model, anova = T)
eta.sq eta.sq.part SS df MS F p
wm.t$cond 0.5821 0.5821 213.0 3 71.013 35.29 2.154e-14
Residuals 0.4179 NA 152.9 76 2.012 NA NA
# Conduct post-hoc tests to evaluate all pairwise comparisons
TukeyHSD(aov.model)
Tukey multiple comparisons of means
95% family-wise confidence level
Fit: aov(formula = wm.t$gain ~ wm.t$cond)
$`wm.t$cond`
diff lwr upr p adj
t12-t08 1.25 0.0716 2.428 0.0333
t17-t08 3.05 1.8716 4.228 0.0000
t19-t08 4.25 3.0716 5.428 0.0000
t17-t12 1.80 0.6216 2.978 0.0008
t19-t12 3.00 1.8216 4.178 0.0000
t19-t17 1.20 0.0216 2.378 0.0443
Conduct a binary logisitc regression
myCsv <- getURL("https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/8272421/stat/stat_one_glm.txt",
ssl.verifypeer = FALSE)
BL <- read.table(textConnection(myCsv), header = TRUE)
head(BL)
subject verdict danger rehab punish gendet specdet incap
1 1 0 2 2 2 2 0 7
2 2 0 0 9 0 6 8 2
3 3 1 6 3 2 10 10 4
4 4 1 1 3 2 3 2 1
5 5 0 0 7 4 1 1 10
6 6 1 10 6 1 8 0 0
# Binary logistic regression
lrfit <- glm(BL$verdict ~ BL$danger + BL$rehab + BL$punish + BL$gendet + BL$specdet +
BL$incap, family = binomial)
summary(lrfit)
Call:
glm(formula = BL$verdict ~ BL$danger + BL$rehab + BL$punish +
BL$gendet + BL$specdet + BL$incap, family = binomial)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.969 -0.932 -0.463 0.891 1.957
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -1.74758 0.91728 -1.91 0.0568 .
BL$danger 0.29339 0.09292 3.16 0.0016 **
BL$rehab -0.18784 0.08140 -2.31 0.0210 *
BL$punish 0.07012 0.07111 0.99 0.3241
BL$gendet 0.18574 0.07733 2.40 0.0163 *
BL$specdet 0.00590 0.07865 0.08 0.9402
BL$incap 0.00353 0.07587 0.05 0.9629
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 138.47 on 99 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 114.06 on 93 degrees of freedom
AIC: 128.1
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 3
confint(lrfit) # CIs using profiled log-likelihood (default for logistic models)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -3.65201 -0.02217
BL$danger 0.11998 0.48756
BL$rehab -0.35426 -0.03283
BL$punish -0.06763 0.21352
BL$gendet 0.03858 0.34394
BL$specdet -0.15006 0.16092
BL$incap -0.14735 0.15284
confint.default(lrfit) # CIs using standard errors
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -3.54542 0.05027
BL$danger 0.11127 0.47550
BL$rehab -0.34738 -0.02831
BL$punish -0.06926 0.20950
BL$gendet 0.03418 0.33730
BL$specdet -0.14824 0.16005
BL$incap -0.14518 0.15224
# Model fit
with(lrfit, null.deviance - deviance) #difference in deviance for the two models
[1] 24.41
with(lrfit, df.null - df.residual) #df for the difference between the two models
[1] 6
with(lrfit, pchisq(null.deviance - deviance, df.null - df.residual, lower.tail = FALSE)) #p-value
[1] 0.0004397
# Wald tests for Model Coefficients Computes a Wald chi-squared test for 1
# or more coefficients, given their variance-covariance matrix.
library(aod)
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 2) #danger
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 10.0, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.0016
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 3) #rehab
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 5.3, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.021
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 4) #punish
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 0.97, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.32
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 5) #gendet
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 5.8, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.016
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 6) #specdet
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 0.0056, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.94
wald.test(b = coef(lrfit), Sigma = vcov(lrfit), Terms = 7) #incap
Wald test:
----------
Chi-squared test:
X2 = 0.0022, df = 1, P(> X2) = 0.96
# Odds ratios
exp(coef(lrfit)) #exponentiated coefficients
(Intercept) BL$danger BL$rehab BL$punish BL$gendet BL$specdet
0.1742 1.3410 0.8287 1.0726 1.2041 1.0059
BL$incap
1.0035
# Classification table
library(QuantPsyc)
# Provides a Classification analysis for a logistic regression model. Also
# provides McFadden's Rsq.
ClassLog(lrfit, BL$verdict)
$rawtab
resp
0 1
FALSE 39 16
TRUE 13 32
$classtab
resp
0 1
FALSE 0.7500 0.3333
TRUE 0.2500 0.6667
$overall
[1] 0.71
$mcFadden
[1] 0.1763
Statistics One is available on coursera